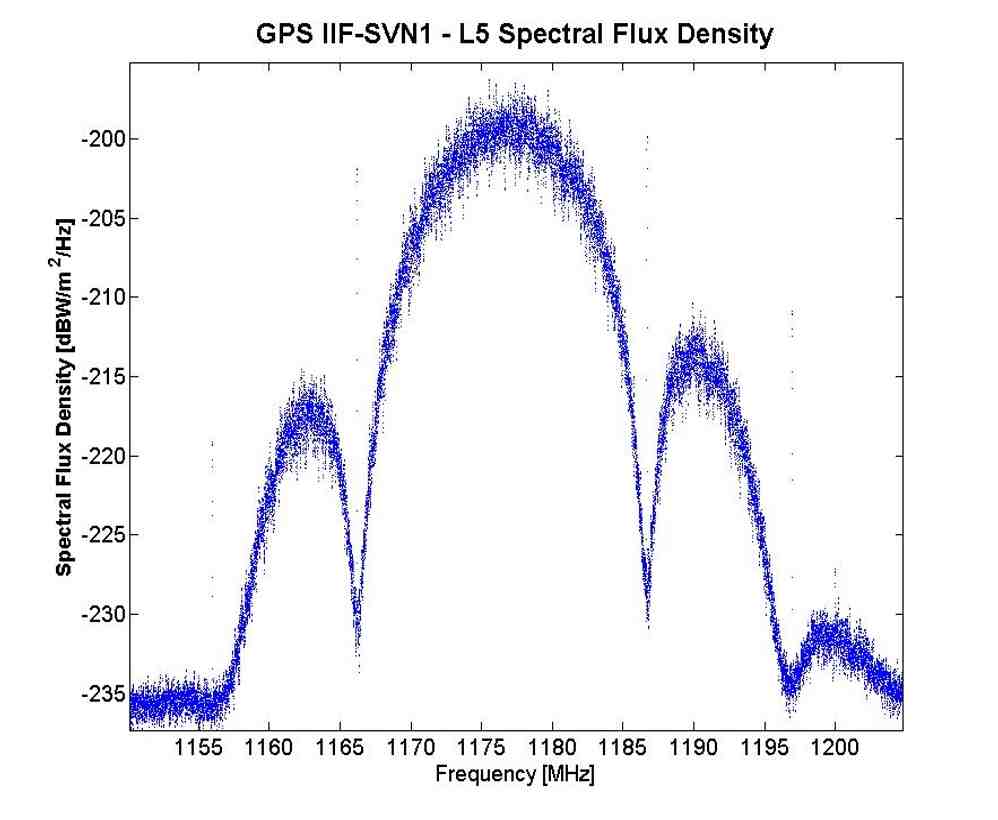
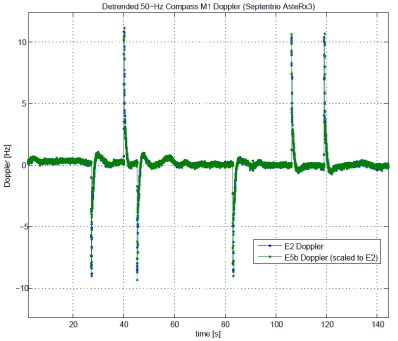
Russian Company Offers ‘Preliminary’ Specifications for GLONASS CDMA Signal
 Illustration of GLONASS-K satellite
Illustration of GLONASS-K satelliteA provisional specification for the planned GLONASS CDMA signal has been defined and is available to receiver manufacturers interested in experimenting with the demonstration signal that will be broadcast from the GLONASS-K satellite to be flight-tested later this year.
Mark Shmulevich, head of business development for Russian Space Systems (RSS), extended the offer at the Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation GNSS Implementation Team (APEC-GIT) meeting in Seattle, Washington, this week. RSS is an amalgamation of 10 former Russian federal state unitary enterprises — that is, government corporations — and other Russian institutes and agencies established last year, with the former Russian Institute of Space Device Engineering (RISDE) serving as the lead.
By Inside GNSS