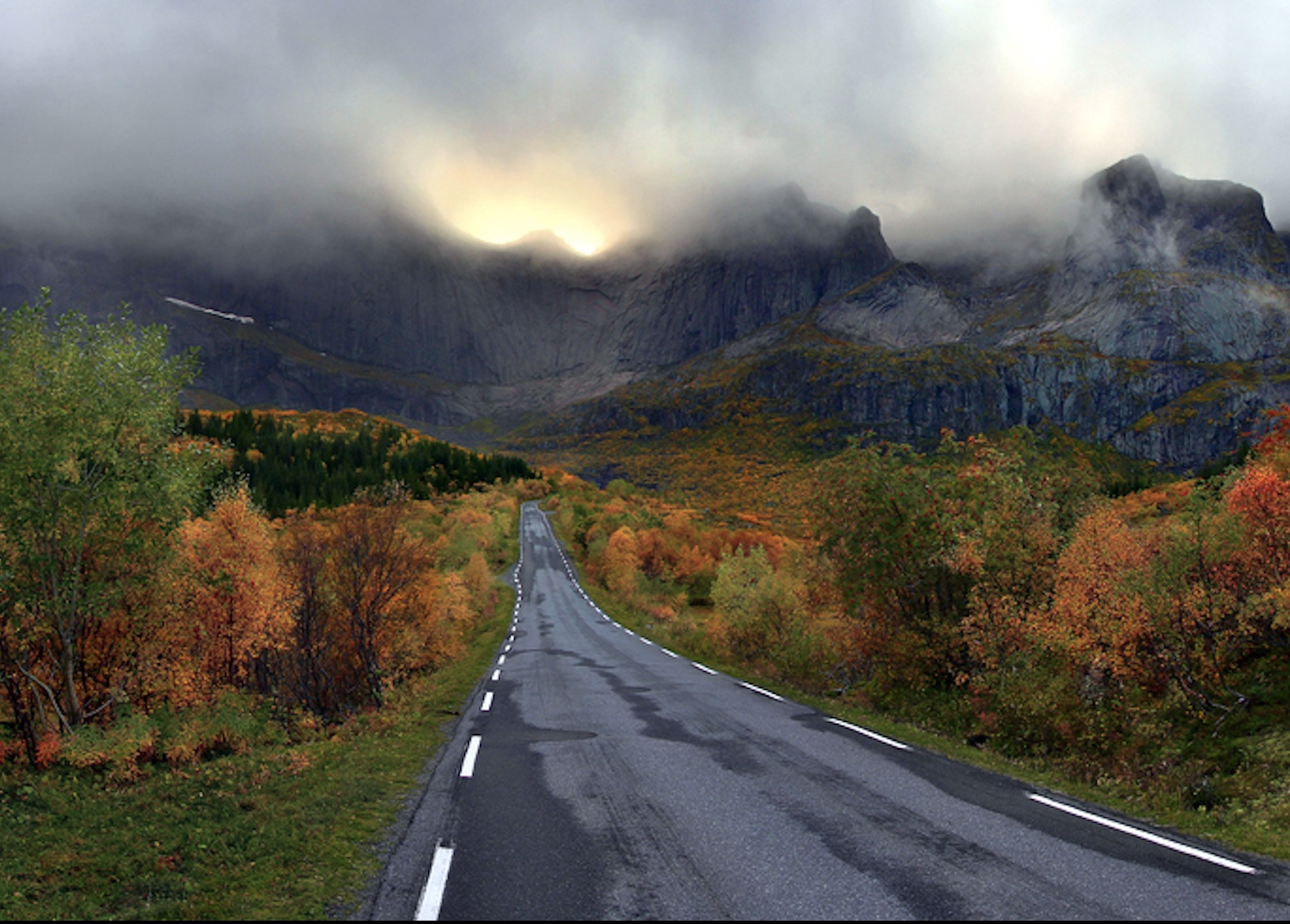
GNSS jamming trials are being carried out on the Island of Andøya, in Northwestern Norway, during Jammertest 2024. The event features both simple and sophisticated, staged spoofing and jamming attacks, allowing participants to identify potential strengths and weaknesses in their GNSS-based systems.
The increasing frequency of jamming and spoofing incidents, particularly affecting Northern Norway and possibly linked to Russian activities, is driving the demand for more resistant GNSS and non-GNSS-based contingency systems. The Norwegian Defense Ministry, for example, has called for the development of alternative means of PNT provision as protection against GNSS jamming in the context of maritime navigation.
During Jammertest 2024, researchers from the public and private sectors are assessing how effectively existing and new technology systems are able to withstand jamming and spoofing attacks in real-world scenarios. One of the staged jamming attacks (4-13 September 2024) is taking place on two stretches of road near Bleik, a small, coastal town on Andøya Island. The trial was approved by Norway’s National Communications Authority and is being carried out by the Public Roads Administration, Defense Research Institute, Norwegian Space Center and other partners.
Rising interest and concern
Later in September 2024, the Defense Research Institute will carry out military jamming tests, also on Andøya, in connection with operational testing of military weapons systems and loss of GPS signals. Authorities have notified local inhabitants that they may experience relatively short-lived GNSS disruption during all of the above-mentioned trials, most of which will involve GPS jamming but not spoofing or meaconing.
This year, 2024, marks the third consecutive year that Jammertest is being held on Andøya, also the site, readers will know, of Norway’s Andøya Space Center. According to organizers, Jammertest 2024 has garnered record-high interest from around the world, with over 300 applicants for the event. During the 2023 edition, 264 comprehensive tests were conducted, exploring various topics such as sensor fusion, radio frequency interference (RFI) countermeasures, and combinations of GNSS with alternative positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) solutions.